Sustainable Living: The Positive Impact of Urban Beekeeping
Urban beekeeping is emerging as a powerful movement within sustainable living, offering both environmental and community benefits. In cities around the world, rooftop hives and community gardens are transforming concrete jungles into vital habitats for pollinators. As urban spaces reclaim their roles in supporting biodiversity, beekeeping stands out as an inspiring example of how city dwellers can make meaningful contributions to environmental health and resilience. This page explores how urban beekeeping positively impacts ecological balance, fosters community connections, advances educational initiatives, and supports local economies.
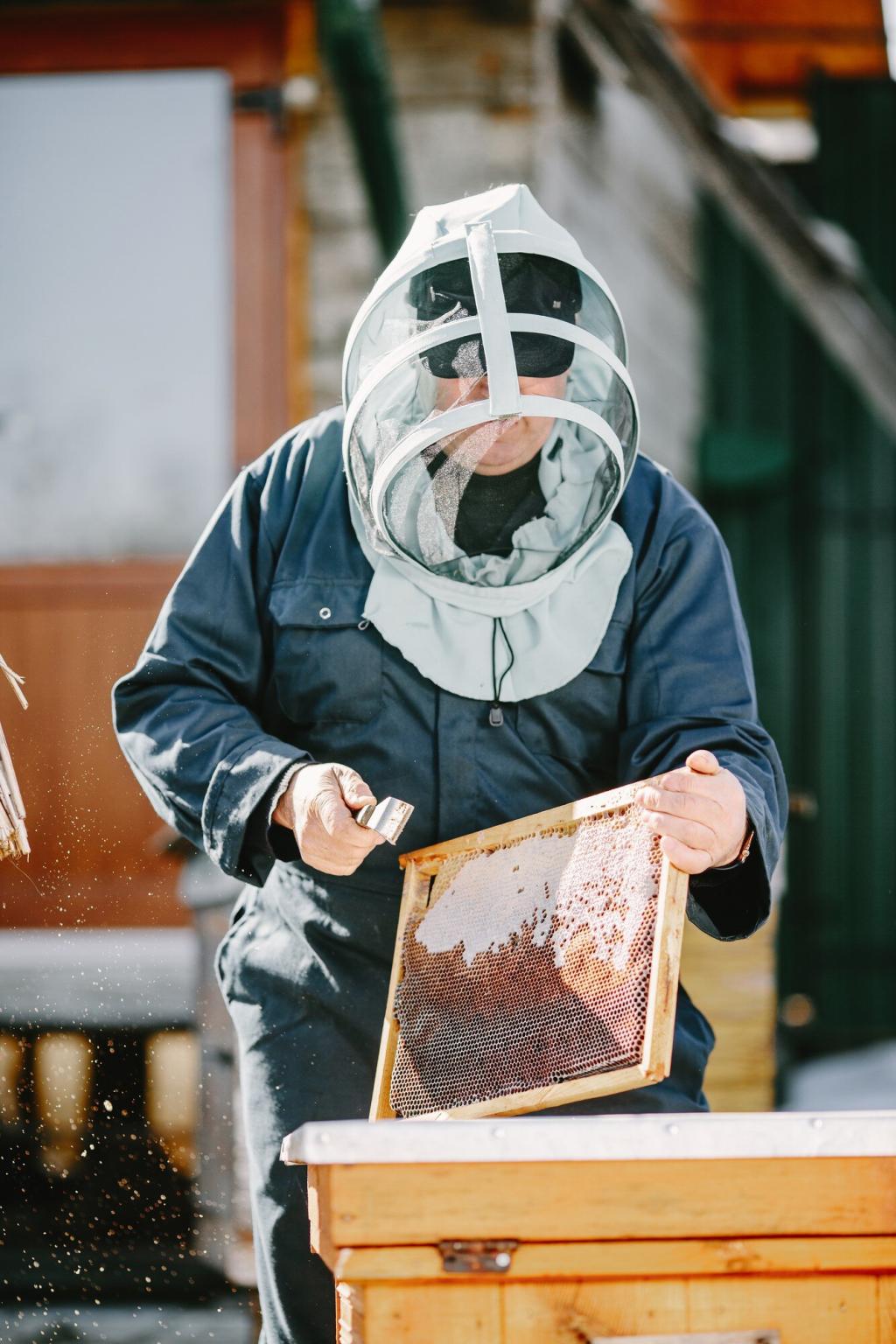
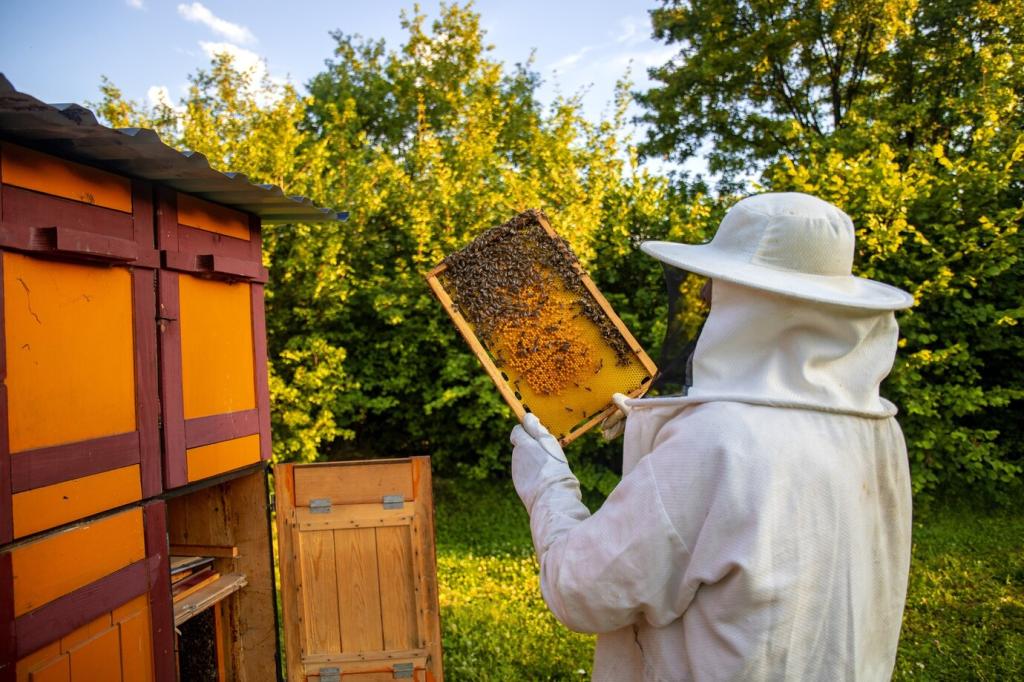


Supporting Pollinator Populations
Honeybee colonies placed on rooftops, balconies, and community gardens introduce essential pollinators to environments where they are often lacking. This boosts the reproduction of flowering plants, cultivates new green spaces, and strengthens the overall health of urban flora. By supporting these populations, urban beekeeping not only helps honeybees but also indirectly aids butterflies, solitary bees, and other native pollinating species. The cumulative effect is a richer, more vibrant tapestry of plant and animal life woven throughout the city.
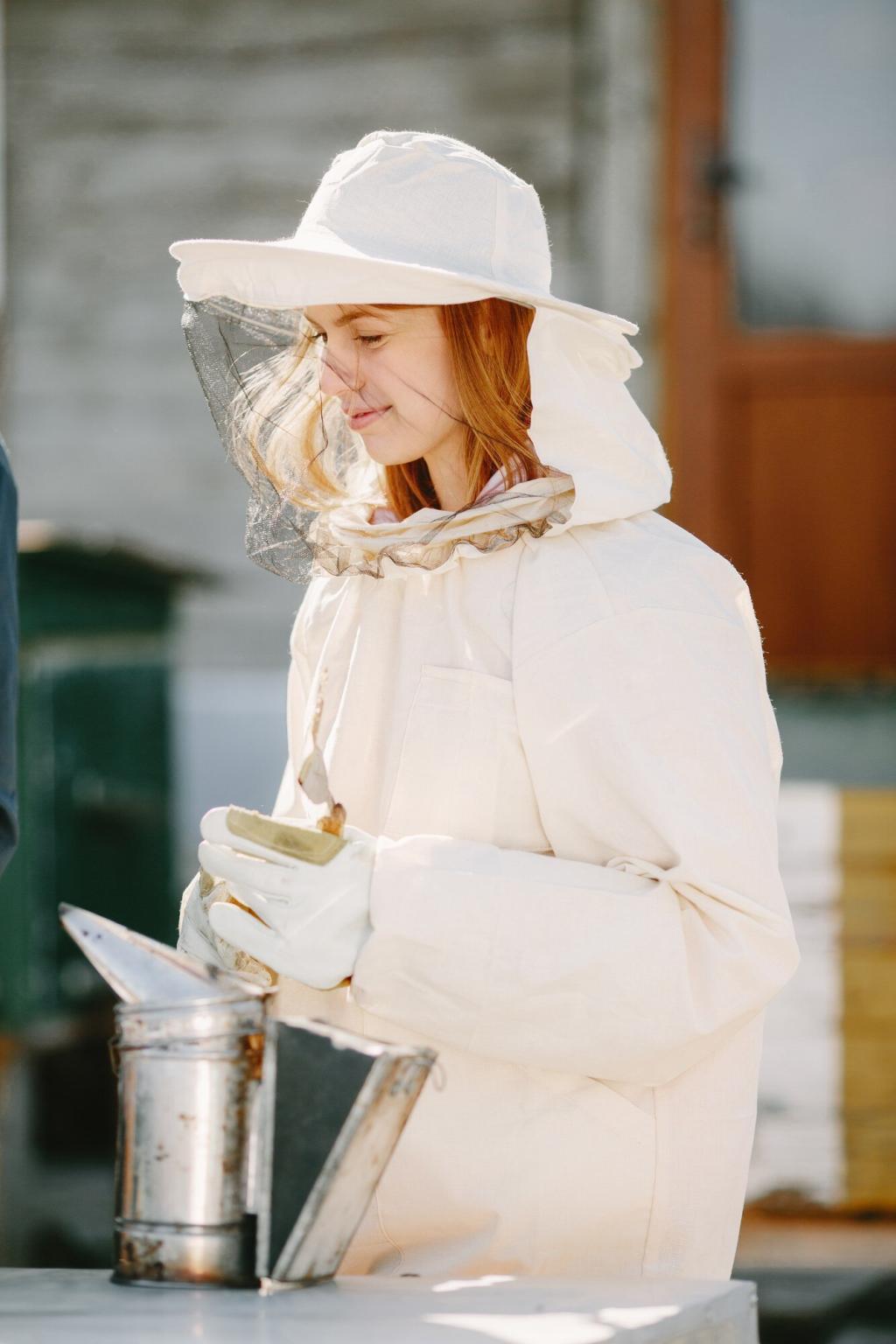

Enhancing Green Spaces
The presence of beehives in cities leads to improved plant pollination, resulting in healthier parks, thriving gardens, and productive urban forests. This synergy between bees and green spaces demonstrates how small-scale interventions can lead to substantial environmental dividends. Managed hives help sustain the growth of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, making the urban environment not only more attractive but also more productive, resilient, and sustainable for future generations.
Strengthening Community Connections
01
Community beekeeping projects serve as a focal point for residents, bringing together individuals across diverse backgrounds. Working together to maintain hives, participants share stories, knowledge, and experiences, creating bonds that might otherwise never form. These endeavors foster mutual respect and collective achievement, nurturing a sense of care and ownership for both bees and their urban environment.
02
Urban beekeeping initiatives often inspire volunteering, attracting individuals who wish to contribute positively to their neighborhoods. Whether tending hives or educating others about pollinators, volunteers play an essential role in these programs. Their engagement builds a culture of stewardship, empowering residents to take active roles in shaping the future of their communities and promoting sustainable living at the grassroots level.
03
Urban apiaries naturally invite the participation of people of all ages. Beekeeping projects frequently involve schools, retirees, and families working together, creating intergenerational exchanges of wisdom and enthusiasm. This collaboration helps preserve traditional skills, encourages mentorship, and builds a legacy of environmental care that transcends age boundaries, uniting city residents in collective action.
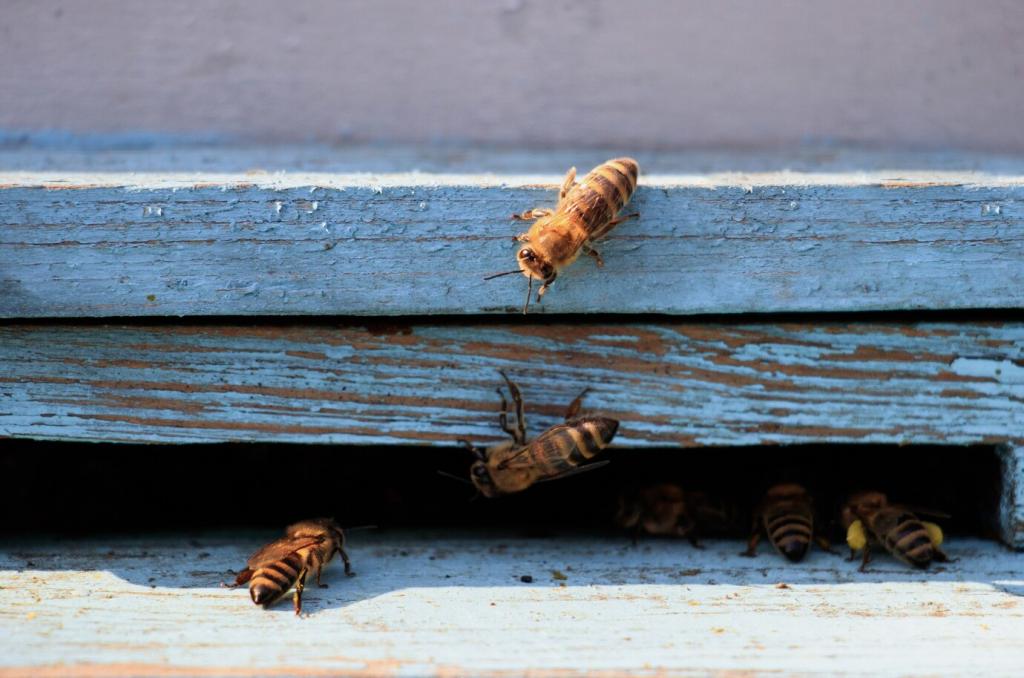

Inspiring Hands-On Learning
Interactive beekeeping experiences provide tangible ways for people to connect with nature, right in the heart of the city. Observing the inner workings of a hive or participating in honey harvests enables learners to witness firsthand the vital roles pollinators play. These educational moments drive home environmental lessons in memorable ways, cultivating curiosity and lifelong learning among participants of all ages.
Raising Awareness of Pollinator Challenges
Through urban beekeeping, city dwellers become more aware of the threats facing bees and other pollinators, including pesticide use, habitat loss, and climate change. Education programs often include information about these issues, helping participants understand the human actions that impact pollinator health. This awareness beckons individuals to make more informed and sustainable choices in their daily lives, amplifying the positive effects of urban beekeeping far beyond the hives themselves.
Encouraging Scientific Inquiry
Cities offer unique research opportunities for scientists and citizen scientists alike, and urban beekeeping provides a rich field for observation and experimentation. Beekeepers and students can monitor hive health, pollination patterns, and environmental quality, contributing valuable data to larger ecological studies. By encouraging scientific curiosity, urban apiaries empower people to take part in real-world ecological research that benefits both science and society.